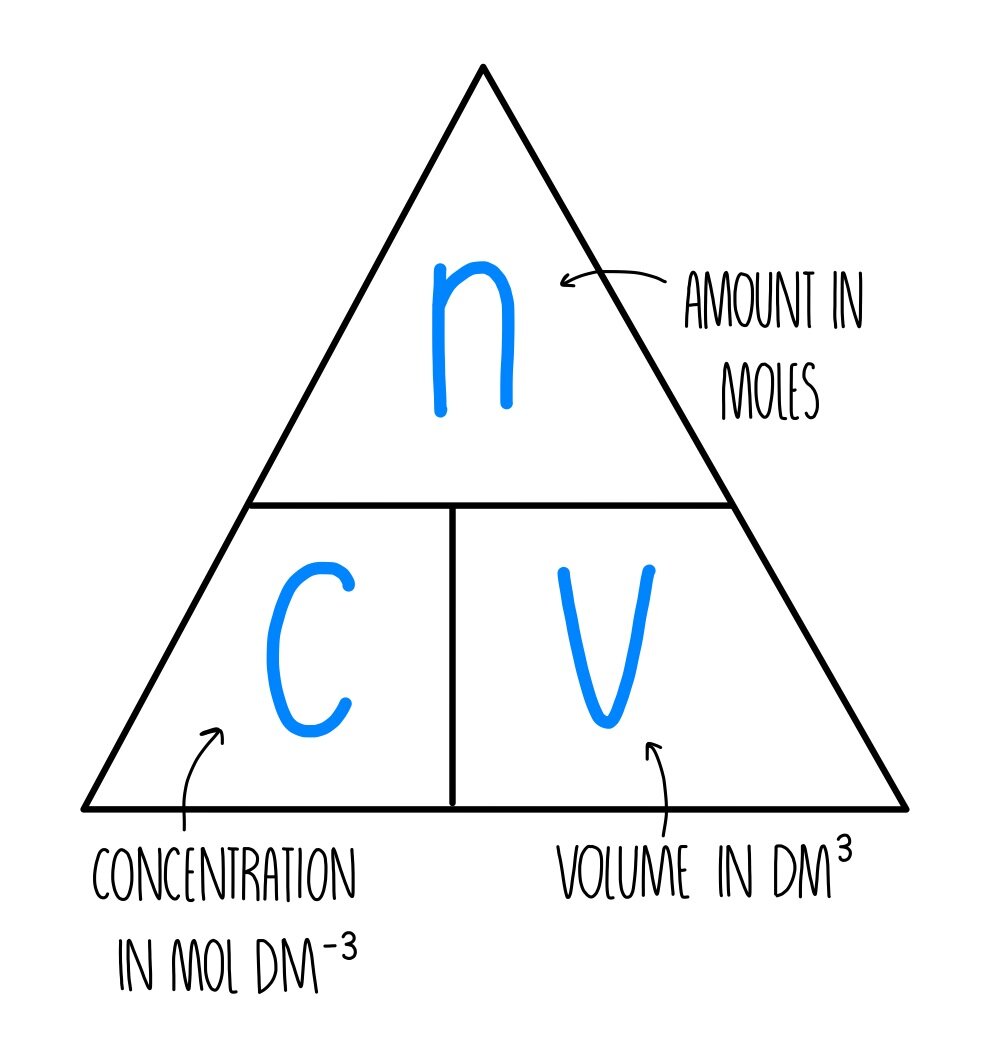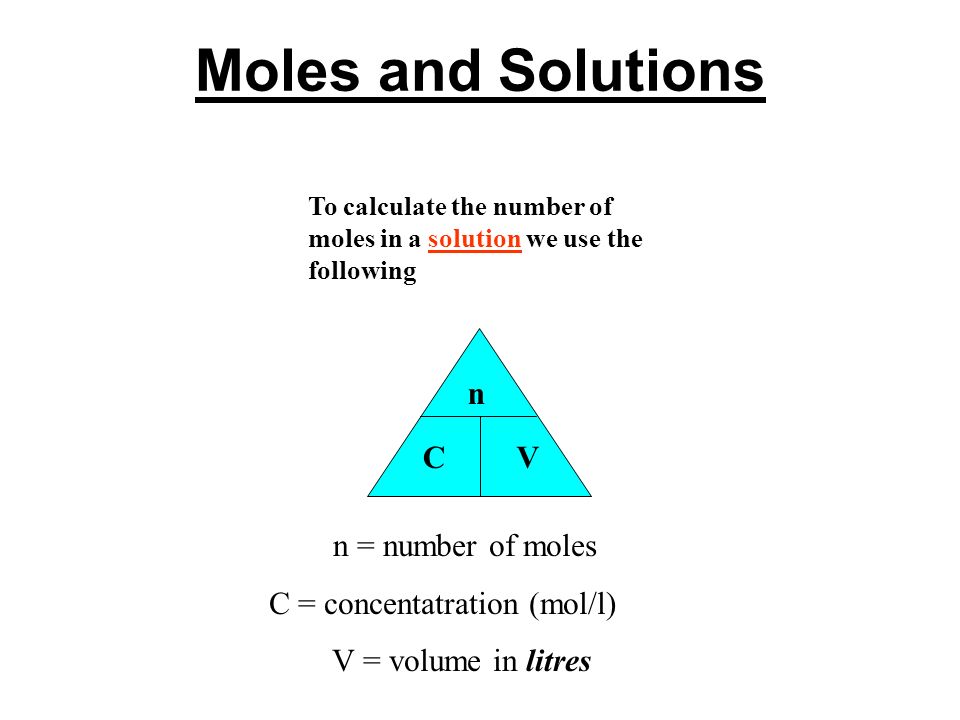
Moles and Solutions g n gfm To calculate the number of moles in a solution we use the following n CV n = number of moles C = concentatration (mol/l) V. - ppt download

Moles and Solutions g n gfm To calculate the number of moles in a solution we use the following n CV n = number of moles C = concentatration (mol/l) V. - ppt download

SOLVED: An ideal gas has a constant molar specific heat cv= 564 J/K/mol. Calculate the change in entropy per mole in going from the state (V1,T1)=(12 m^3,19 C) to the state (V2,T2)=(551
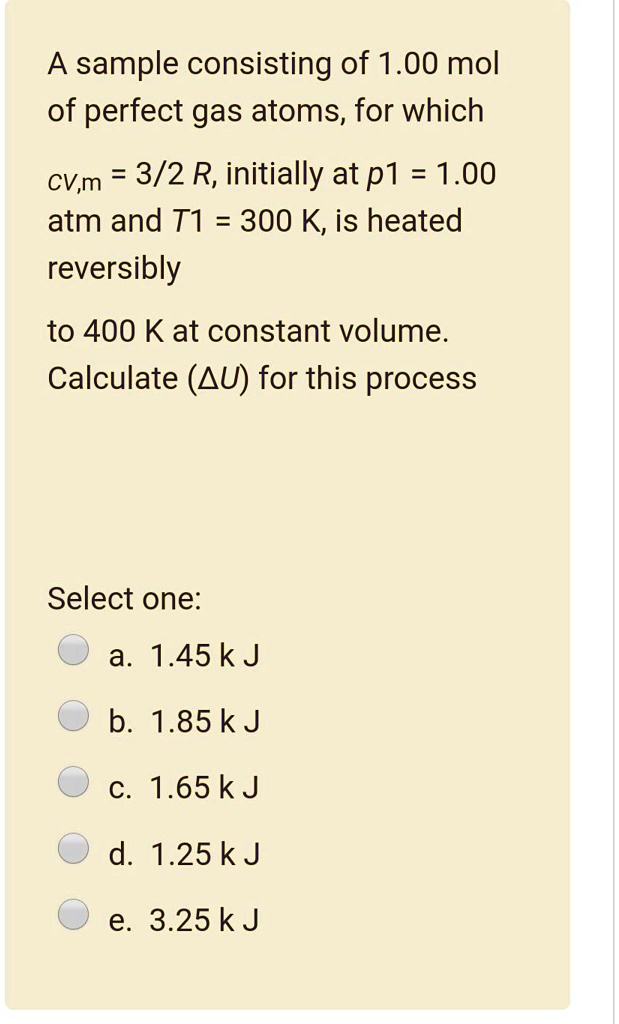
SOLVED: A sample consisting of 1.00 mol of perfect gas atoms, for which CVm = 3/2 R, initially at p1 1.00 atm and T1 = 300 K, is heated reversibly to 400

SOLVED: For an ideal gas CV and Cp are different because of the workW associated with the volume change for a constant-pressure process.To explore the difference between CV and Cp for a
The CV (a) and CA (b) curves for the electrochemical oxidation of 0.5... | Download Scientific Diagram

a Comparison of CV measurements recorded in (LiCl–KCl)(eut.)–0.09 mol%... | Download Scientific Diagram

A) CV curves of 0.04 mol L À 1 BR buffer (pH 4.0) with 5 % of DMSO (À... | Download Scientific Diagram

Moles and Solutions g n gfm To calculate the number of moles in a solution we use the following n CV n = number of moles C = concentatration (mol/l) V. - ppt download

The Mole And Concentration Formula Triangle Isolated On White Relationship Between Concentration Moles And Volume Cnv Stock Illustration - Download Image Now - iStock
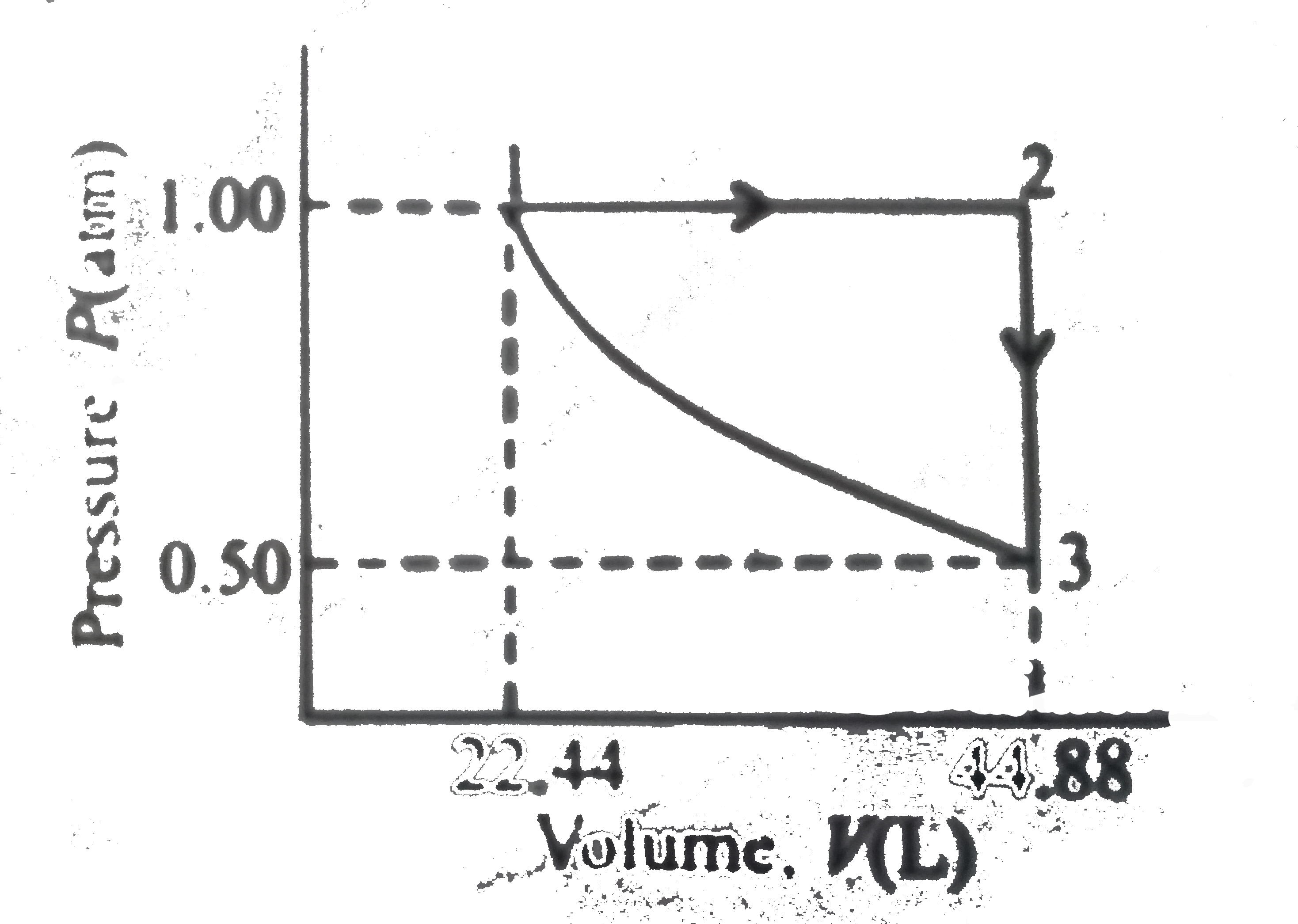
A sample consisting of 1mol of a mono-atomic perfect gas (C(V) = (3)/(2)R) is taken through the cycle as shown. Temperature at points (1),(2) and (3) respectively is

![CV for a 2 mol·dm⁻³, b 1 mol·dm⁻³ and c 0.5 mol·dm⁻³ [PMIM][Tf2N]... | Download Scientific Diagram CV for a 2 mol·dm⁻³, b 1 mol·dm⁻³ and c 0.5 mol·dm⁻³ [PMIM][Tf2N]... | Download Scientific Diagram](https://www.researchgate.net/publication/332751775/figure/fig3/AS:961858655764491@1606336382353/CV-for-a-2moldm-b-1moldm-and-c-05moldm-PMIMTf2N-solutions-at-different.png)